Video
Below is a quick video snap shot of this article.
Definition
When there is a normal PR interval, but at times conduction through the AV node fails.
A key here is that the PR interval should be normal and the P to P interval should be regular. That is to say the distance from on P to the next should be the same length for all P waves on the strip.
I like to think of this as seeing P waves marching through the strip while there are times when there are missing QRS complexes.
A good way I remember this is with the statement “if P’s are marching through, then you got a Mobitz 2.”
What’s happening in the heart
Atrial Contraction
First, the impulse originates in the SA node just as it does with a normal sinus rhythm.
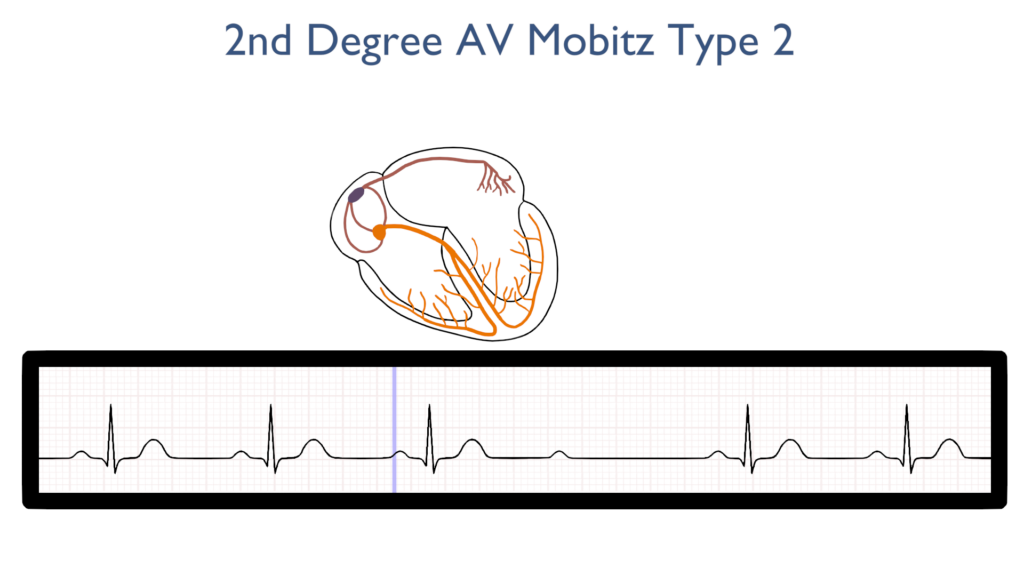
AV Node Delay
Next, there is a delay in the AV node just as there is with a normal sinus rhythm but at times conduction will fail to pass through the AV node onto the bundle of HIS.
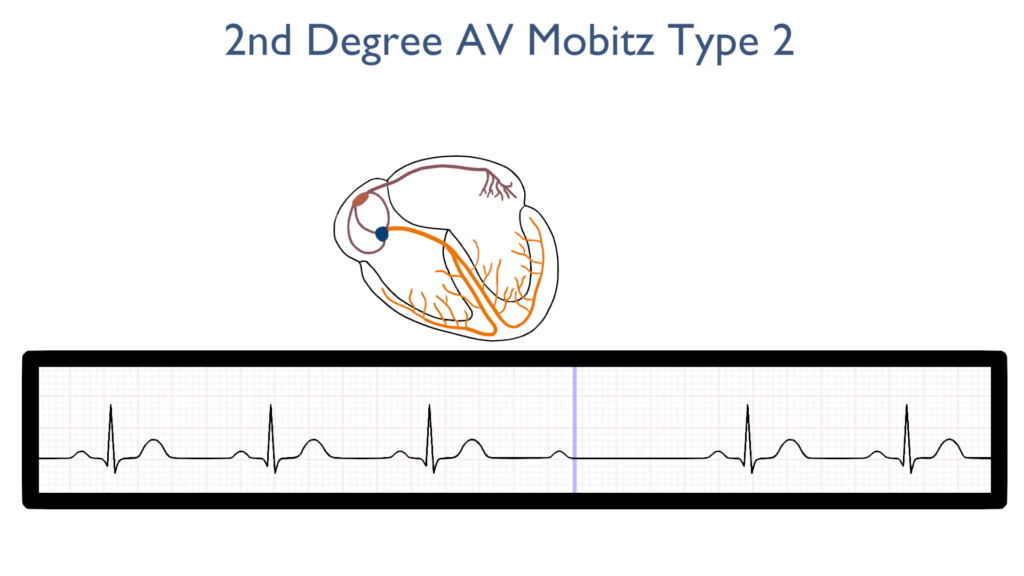
Ventricular Contraction
Next, when the impulse does pass through the AV node the QRS should be normal.
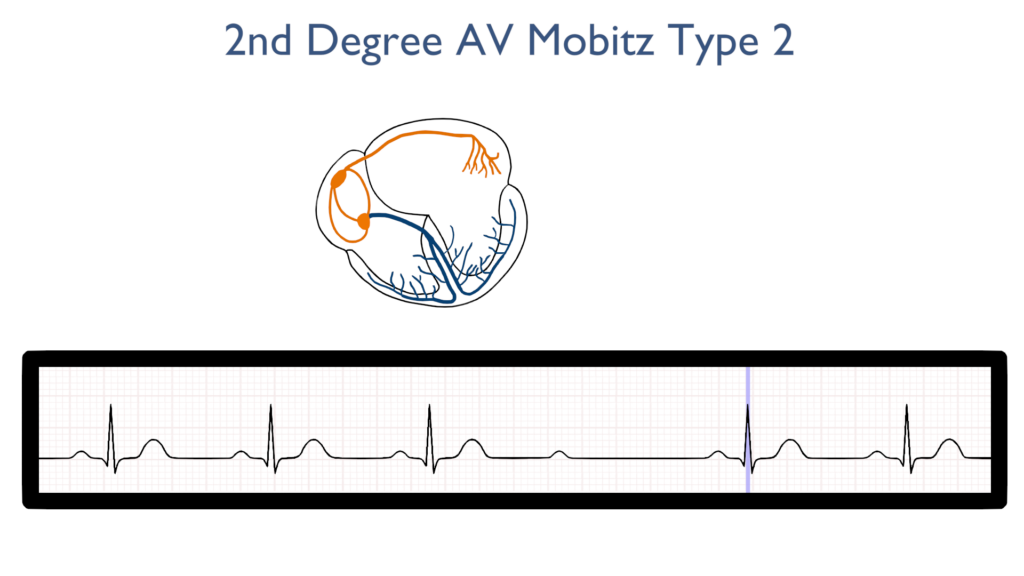
Ventricular Repolarization
Lastly, the ventricles relax and reset for the next contraction.
T waves should be normal.
Seven steps of rhythm interpretation
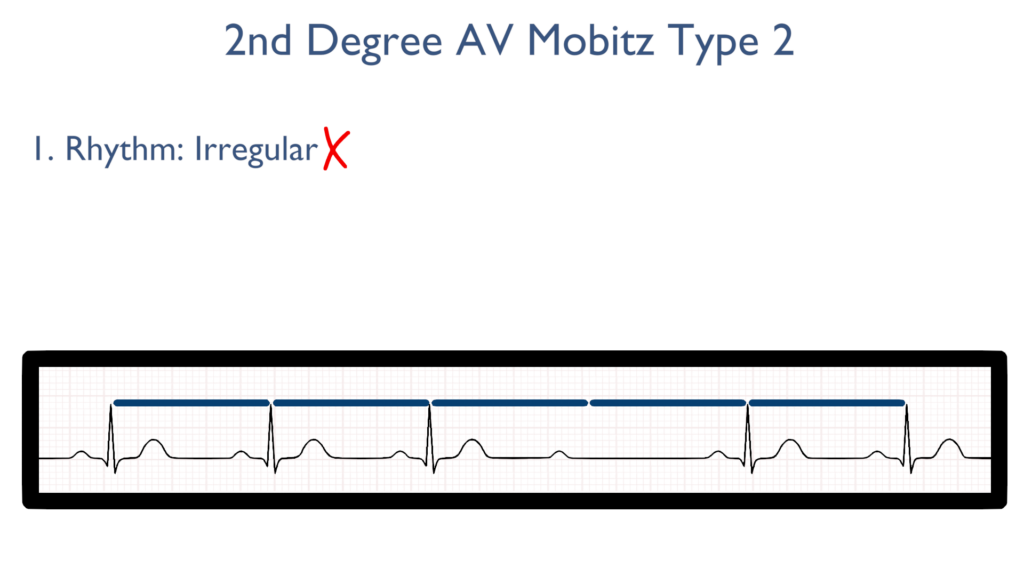
1. Assess the rhythm.
First, the rhythm may be regular or just slightly irregular.
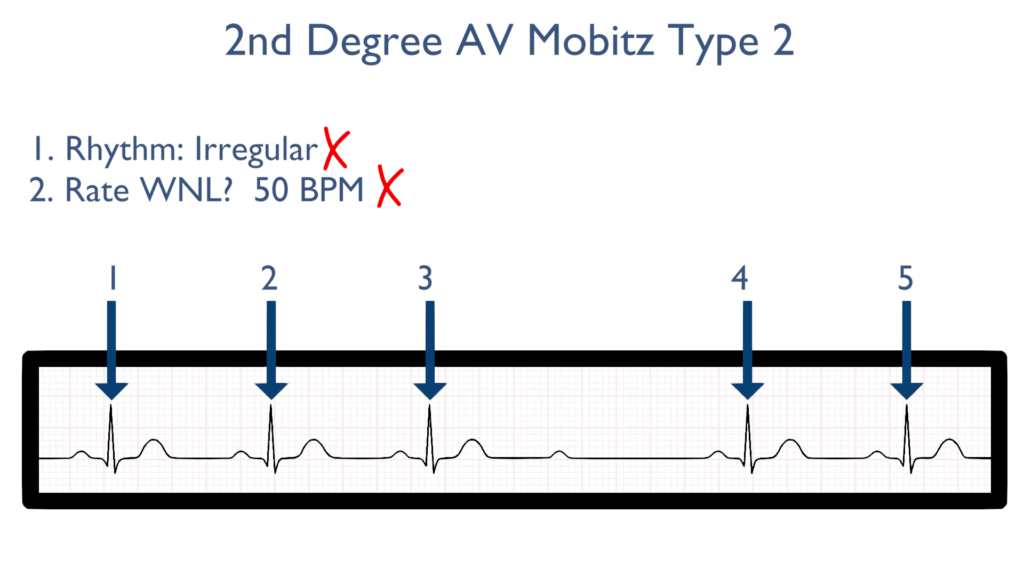
2. Assess the rate.
Next, when assessing the rate you will find it will be variable like the rhythm. The rate may be regular or brady.
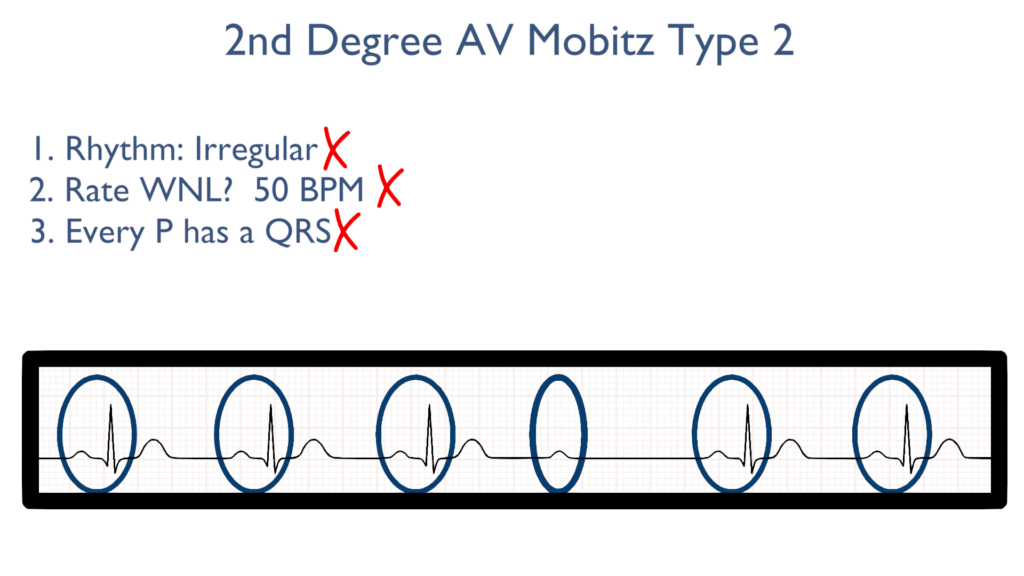
3. Assess atrial and ventricular rates.
When it comes to assessing atrial and ventricular rates there will be more P’s than there are QRS waves.
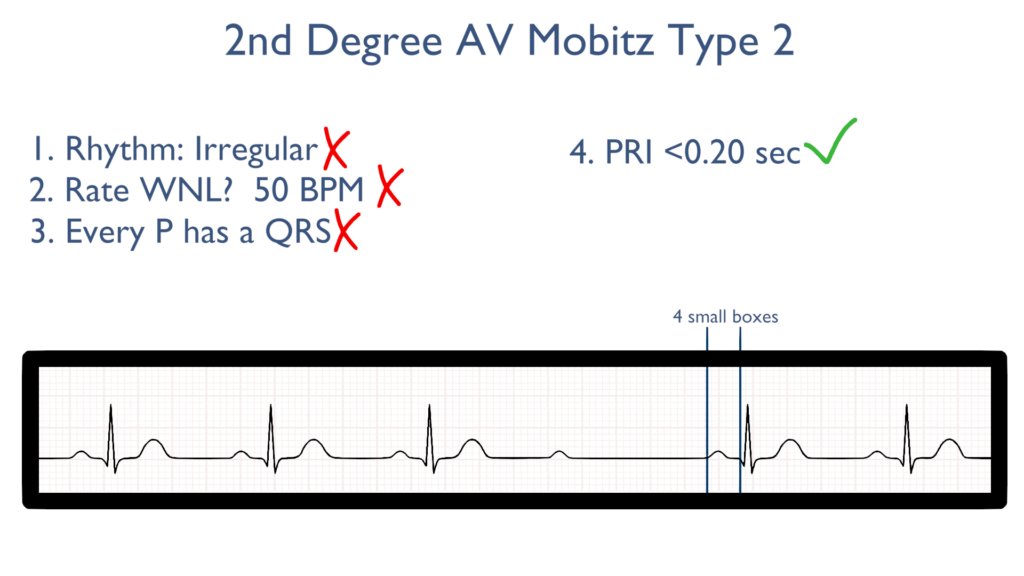
4. Assess the P waves and PR interval.
The PR Interval should be WNL.
There should be no variations in the PR Interval such as there were with the Wenckebach.
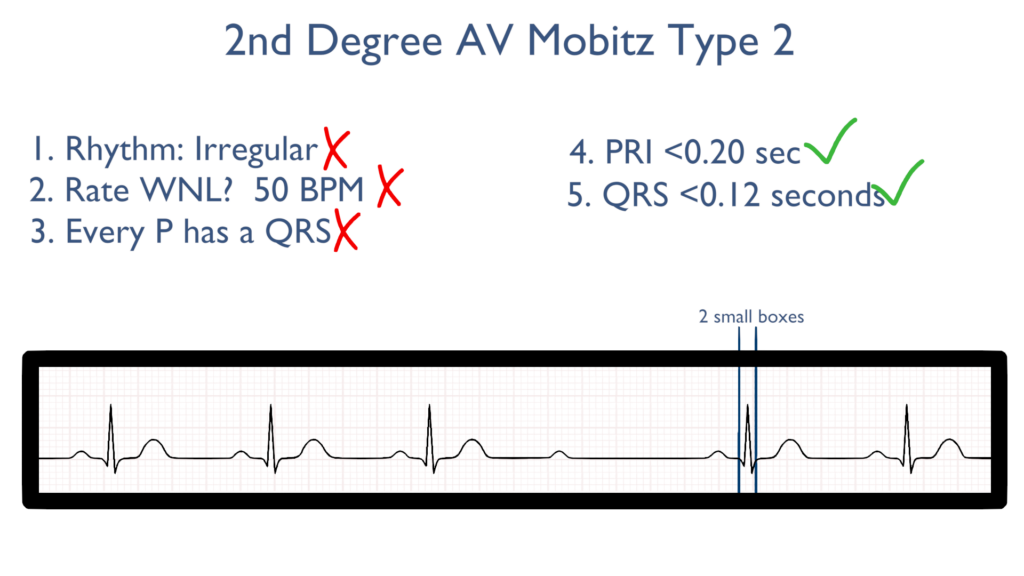
5. Assess the QRS.
Next the QRS will be within normal limits.
The QRS should be between 0.06 seconds to 0.12 seconds.
Better yet, QRS should be between 1.5 to 3 small boxes.
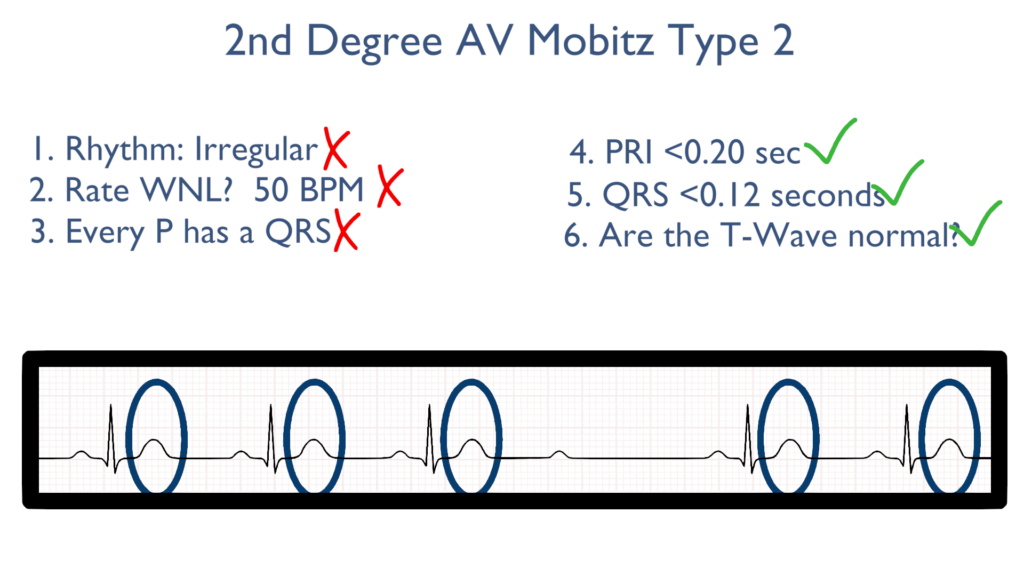
6. Assess the T waves.
T waves should deflect in the positive direction with no ST-Elevation or ST-Depression.
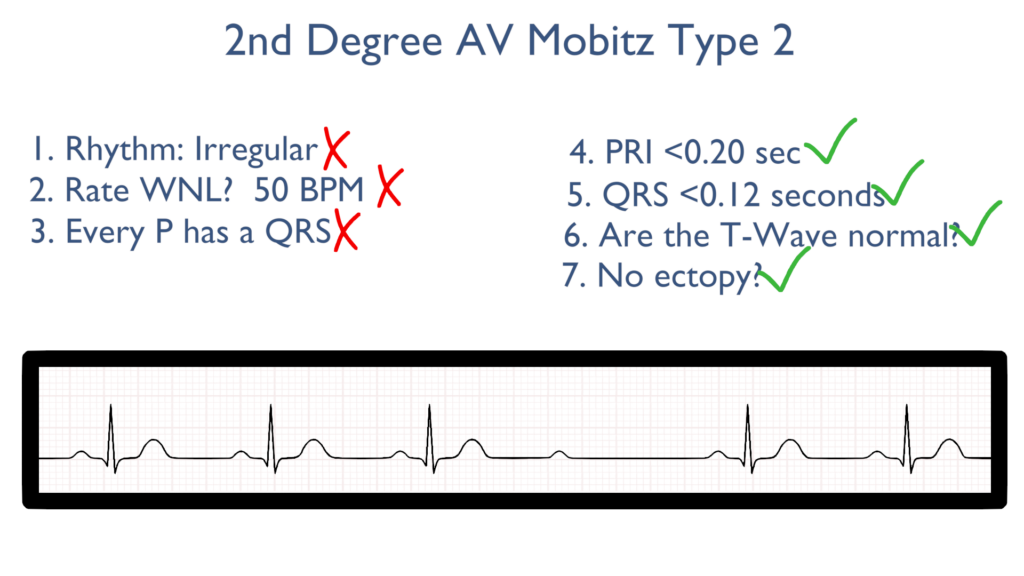
7. Assess for Ectopy.
As you can see on this 6 second strip there are no ectopic beats. This is to say there are no PVC’s or PAC’s present.
Treatments for Mobitz 2
Special Consideration
Mobitz 2 blocks will often lead to a Type 3 Complete AV block.
Mobitz 2 blocks should be treated once they are identified.
Treatments for Stable and Unstable patients
Medications:
Atropine. (Note: in most cases atropine will be ineffective)
